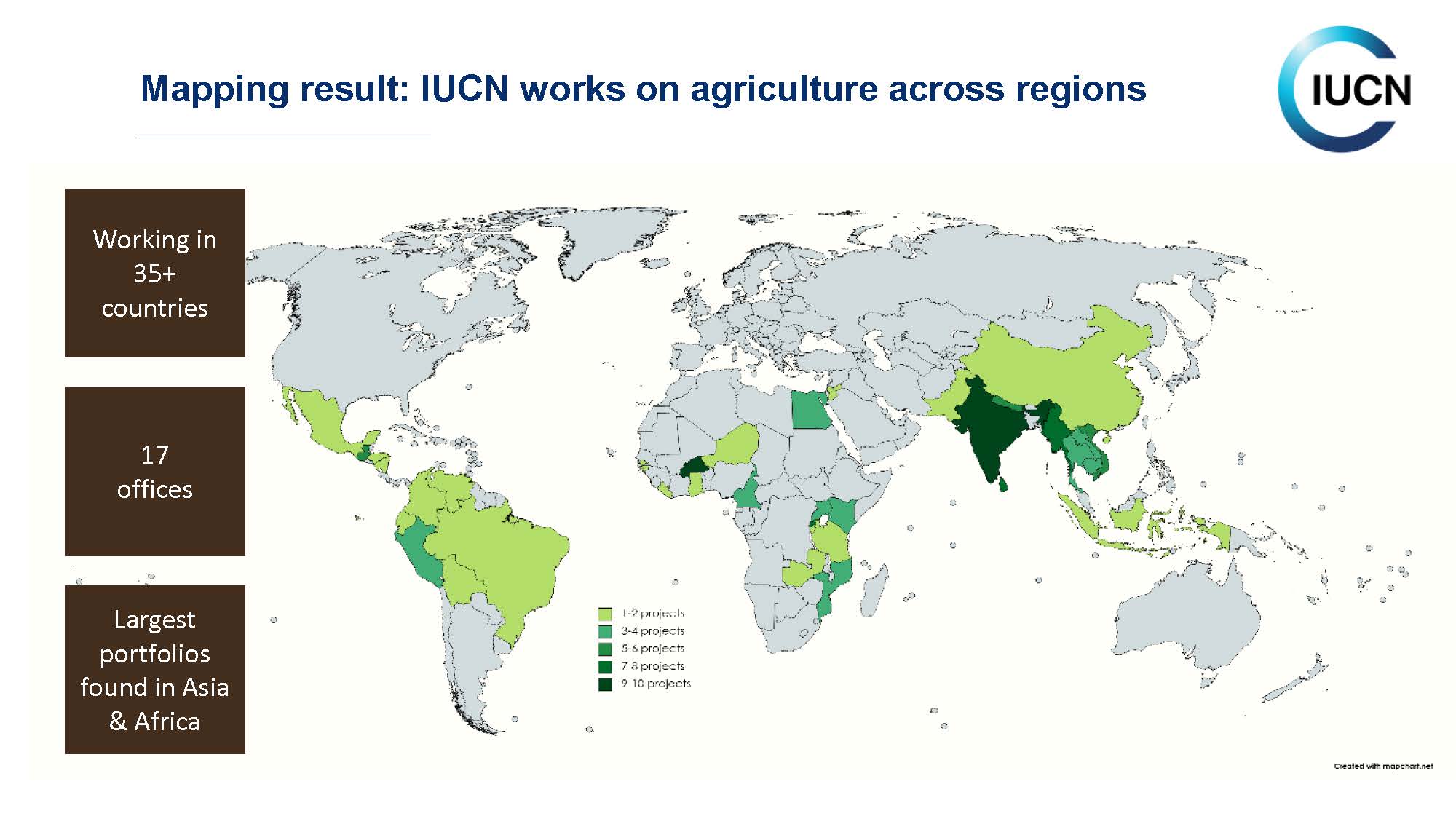
IUCN engagement in agriculture and soil biodiversity
IUCN has developed a new engagement in agriculture, guided by the vision of a future where biodiversity is restored and conserved on farms and in agricultural landscapes as nature-based solutions to global challenges and human and societal needs, contributing to the transition towards sustainable and resilient societies.
The goal of this programmatic engagement is to foster dialogue between agriculture and conservation sectors, and encourage governments, businesses and land managers (including farming communities) implement a common vision to protect and restore biodiversity on farms and in agricultural landscapes, including the ecosystems on which agriculture depends.
In January 2021, the IUCN Director General launched a global initiative on agriculture and land health meant to boost the implementation of this agriculture programme across IUCN activities.
 Photo: IUCN
Photo: IUCN